Introduction
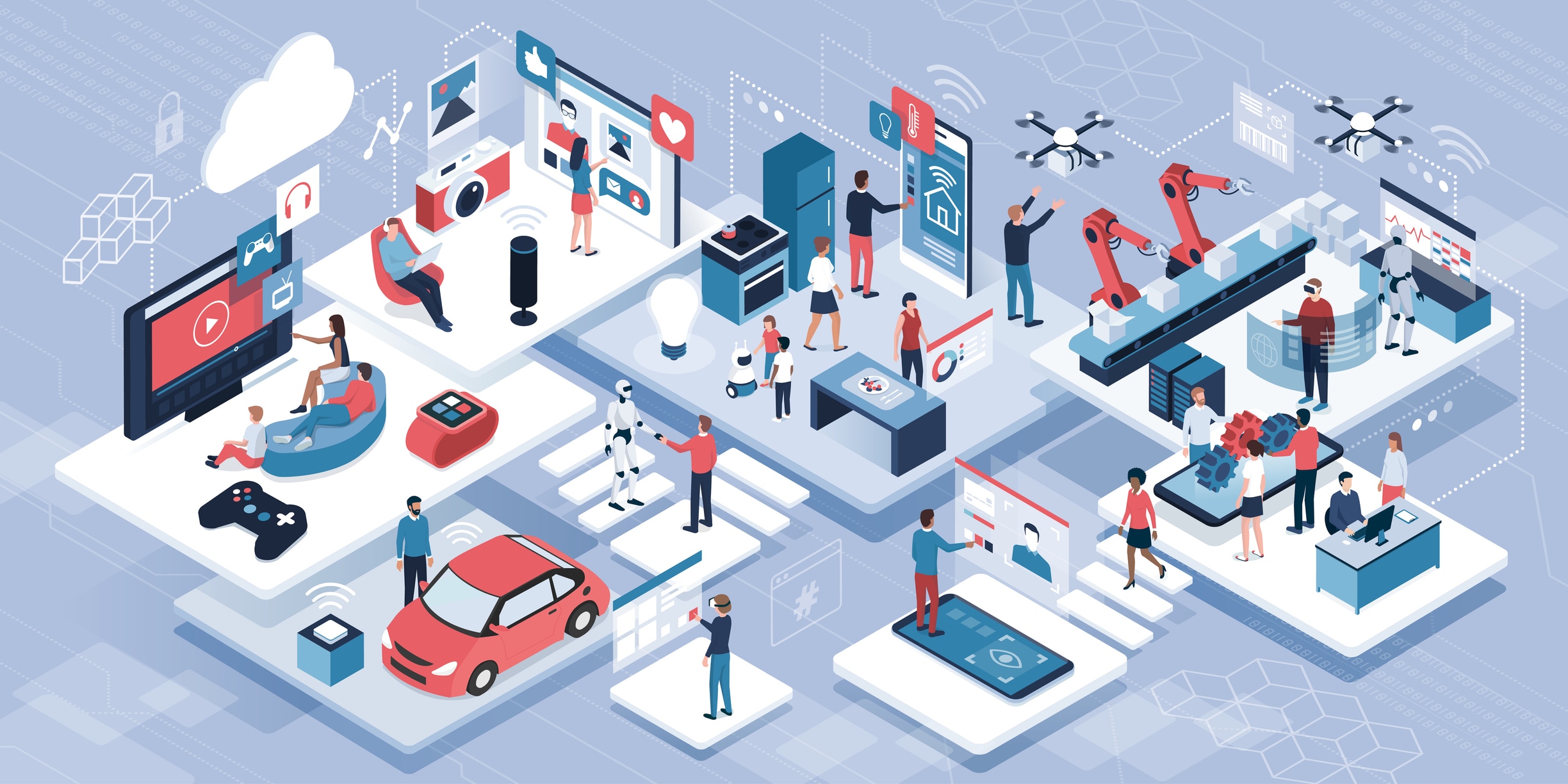
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly growing concept that is reshaping how we live and work. Simply put, IoT refers to the interconnection of everyday objects—devices, vehicles, appliances, and more—through the internet, allowing them to send and receive data. This network of smart, connected devices has the potential to transform industries, homes, and even cities. But what exactly is IoT, and why is it so impactful?
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things is a system where physical devices are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to connect and exchange data over the internet. These devices, often referred to as “smart” devices, can range from simple household items like refrigerators and thermostats to complex machinery used in manufacturing.
IoT devices can communicate with each other, gather and analyze data, and perform automated actions without requiring human intervention. This makes processes more efficient, enhances user experiences, and creates new opportunities for businesses and consumers alike.

How Does IoT Work?
At the heart of IoT is data collection and communication. The process typically involves three key steps:
- Sensors and Devices: IoT devices are equipped with sensors or hardware that can detect and collect information from their environment. This data can be as simple as temperature readings or as complex as video footage from a security camera.
- Connectivity: Once data is collected, it needs to be transmitted to a central hub or cloud platform where it can be processed. IoT devices use various communication methods like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and more to send and receive data.
- Data Processing and Action: After the data is received, it is analyzed, and a response or action can be triggered. For example, a smart thermostat might use temperature data to automatically adjust the heating or cooling of a home.
Applications of IoT
IoT is being implemented across a wide range of industries, transforming how businesses and consumers operate. Here are some of the most common applications:
- Smart Homes: One of the most popular uses of IoT is in smart home devices such as smart lights, thermostats, and security systems. These devices allow homeowners to monitor and control their homes remotely via smartphones, providing convenience and energy savings.
- Healthcare: IoT in healthcare is revolutionizing patient care. Wearable devices like smartwatches can monitor vital signs and send alerts in case of irregularities. IoT-enabled medical equipment can also assist doctors in diagnosing and monitoring patients more effectively.
- Transportation and Automotive: Connected cars are equipped with IoT sensors that provide real-time data on vehicle performance, enabling predictive maintenance, improving safety, and enhancing the driving experience. IoT is also used in logistics to track and manage fleet movements efficiently.
- Agriculture: IoT has found a place in agriculture, where smart sensors monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. Farmers can use this data to optimize irrigation, reduce waste, and increase crop yields.
- Smart Cities: IoT is driving the development of smart cities, where systems like traffic lights, waste management, and public transportation are connected and optimized to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the quality of life for residents.
- Manufacturing: IoT is at the core of Industry 4.0, where factories use interconnected machinery to monitor production lines in real-time, predict maintenance needs, and reduce downtime. This improves productivity and reduces operational costs.
Advantages of IoT
The Internet of Things brings numerous benefits to both businesses and consumers:
- Efficiency: IoT enables automated processes, reducing the need for manual intervention. Devices can communicate with each other and make decisions based on real-time data, leading to more efficient operations.
- Cost Savings: With IoT, businesses can streamline operations, reduce downtime through predictive maintenance, and optimize resource usage. For consumers, IoT devices like smart thermostats can reduce energy consumption, resulting in lower bills.
- Improved Decision-Making: IoT generates vast amounts of data that, when analyzed, can offer valuable insights. This helps companies make informed decisions, whether in optimizing supply chains or enhancing customer experiences.
- Convenience and Control: IoT devices provide users with greater control and convenience. For instance, smart home devices allow homeowners to adjust settings remotely, monitor energy use, and increase home security—all from a smartphone.
Challenges of IoT
While IoT presents numerous advantages, it also comes with certain challenges:

- Security Risks: As more devices are connected to the internet, the potential for cyberattacks increases. Hackers could exploit vulnerabilities in IoT systems to access sensitive data or even take control of devices.
- Privacy Concerns: IoT devices collect vast amounts of personal data. If not properly secured, this data can be misused, raising concerns about privacy and surveillance.
- Interoperability: With a variety of devices, platforms, and communication standards, ensuring that IoT devices can seamlessly work together can be challenging.
- Infrastructure Needs: IoT relies heavily on fast and reliable internet connectivity. In regions with poor infrastructure, implementing IoT on a large scale may not be feasible.
The Future of IoT
As technology continues to advance, the Internet of Things is expected to grow exponentially. By 2030, it is estimated that there will be more than 75 billion connected devices globally. IoT will play a key role in creating more efficient, sustainable, and connected environments.
Innovations like 5G networks will provide the infrastructure needed to support more IoT devices, while advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will enable devices to process and act on data more intelligently. The potential applications of IoT are endless, from fully autonomous vehicles to personalized healthcare and beyond.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is transforming the way we interact with the world around us, making our lives more convenient, efficient, and connected. While there are challenges to overcome, the benefits of IoT are clear, and its impact on industries and daily life will only continue to grow. As the technology evolves, IoT will play a vital role in shaping the future of smart homes, cities, businesses, and much more.